物理的なマルチボード アセンブリの作成
Altium Designer は、multi-board assembly と呼ばれるマルチボード・アセンブリの作成をサポートしています。マルチボード回路図(*.MbsDoc)でシステムの論理構造を定義したら、次に空のマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメント(*.MbaDoc)へシステム設計を転送して、物理的なマルチボード設計を作成します。この処理により、マルチボード回路図内の各論理ブロックで参照されている物理表現(PCB および他のマルチボード・アセンブリ)がマルチボード・アセンブリ・エディタに読み込まれます。このページでは、その手順について説明します。
マルチボード・アセンブリの論理設計段階の詳細は、ページ Capturing the Logical System Design を参照してください。
新しいマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメントを作成するには:
-
Projects パネルでプロジェクト項目を右クリックし、コンテキストメニューから Add New to Project » Multi-board Assembly を選択して、マルチボード・プロジェクトに新しいマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメント(
*.MbaDoc)を追加します。 -
新しいマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメントを保存します(Projects パネルでその項目を右クリックし、コンテキストメニューから Save As を選択)。
-
マルチボード回路図からマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメントへ、システムの論理表現を転送します – learn more.
-
筐体が利用可能な場合は、アセンブリに読み込みます – learn more.
-
アセンブリ内で各要素を配置します – 詳細は Positioning & Orienting Your Boards ページを参照してください。
-
メイトを使用してアセンブリ内の要素を接続します – 詳細は Working with Mates ページを参照してください。

マルチボード・アセンブリの例。複数の接続された PCB が筐体内に配置されています。
システム設計をマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメントへ転送する
マルチボード設計は、次のいずれかのコマンドを使用して、マルチボード回路図からマルチボード・アセンブリ・ドキュメントへ転送します。
-
Design » Update Assembly - <MultiBoardAssemblyDocumentName>.MbaDocマルチボード回路図エディタのメインメニューから。
-
Design » Import Changes From <MultiBoardProjectName>.PrjMbdマルチボード・アセンブリ・エディタのメインメニューから。
これらのコマンドのいずれかを実行すると、ソフトウェアはマルチボード回路図上の各モジュールを調査し、各子プロジェクトに対して選択されている PCB/アセンブリを特定し、それらのボードをアセンブリに追加するために必要な変更の一覧を Engineering Change Order ダイアログに表示します。

各 PCB プロジェクトのボードは ECO の変更として一覧表示され、ECO を実行するとマルチボード・アセンブリ・エディタに読み込まれます。
![]() ボタンをクリックすると、ボード/アセンブリがマルチボード・アセンブリ・エディタに読み込まれます。各ボード/アセンブリは、子プロジェクト内と同じ向きで設計空間に配置されます。この処理では、各 PCB の完全なデータセットを解析して読み込む必要があるため、時間がかかります。
ボタンをクリックすると、ボード/アセンブリがマルチボード・アセンブリ・エディタに読み込まれます。各ボード/アセンブリは、子プロジェクト内と同じ向きで設計空間に配置されます。この処理では、各 PCB の完全なデータセットを解析して読み込む必要があるため、時間がかかります。

このマルチボード・アセンブリのボードがマルチボード・アセンブリ・エディタの設計空間に読み込まれ、配置の準備ができた状態。
マルチボード・アセンブリへの追加オブジェクトの追加
マルチボード回路図で参照されている PCB に加えて、追加のオブジェクトをマルチボード・アセンブリに読み込むこともできます。追加オブジェクトは、Design メニュー、または Multi-board Assembly パネル上部にあるボタンから読み込めます。

適切なコマンドまたはボタンを使用して、次を実行します:
-
Insert PCB Part – 別の PCB をこのアセンブリに挿入します。
-
Insert MBA Part – 別のマルチボード・アセンブリをこのアセンブリに挿入します。
-
Insert STEP Part – STEP 形式の機械モデルをこのアセンブリに挿入します。
アセンブリ部品の更新または編集
部品のロック/ロック解除
部品をロック/ロック解除するには、対象の部品を選択して右クリックし、コンテキストメニューの Lock Selected Part/Unlock Selected Part コマンドを選択して、アセンブリ・エディタの設計空間における現在位置で部品(またはメイトされた部品)をロック/ロック解除します。別の方法として、Multiboard Assembly パネルで部品項目を右クリックし、Locked を選択します。
-
ロックされた部品は編集/移動できません。
-
ロックされた部品には、Multiboard Assembly パネルで南京錠アイコンが表示されます。
-
ロックされた単体部品には、オブジェクト・ギズモが表示されません(オブジェクト・ギズモの詳細は Positioning & Orienting Your Boards ページを参照してください)。
-
ロックされた部品は、ソース(移動するオブジェクト)として選択されている場合はメイトできません(部品のメイトの詳細は Working with Mates ページを参照してください)。
部品の更新
アセンブリに追加した部品または 3D ボディが更新された場合、次のいずれかの操作で更新内容をマルチボード・アセンブリに読み込めます:
-
メインメニューから Edit » Update All Parts コマンドを選択するか、設計空間の任意の場所を右クリックしてコンテキストメニューから Update All Parts コマンドを選択します(ショートカット:
Shift+Ctrl+U)。これにより、アクティブなマルチボード・アセンブリ内のすべての部品が、対応する子 PCB ドキュメントの最新レイアウト情報で更新されます。 -
必要な部品を選択し、メインメニューから Edit » Update Selected Part コマンドを選択するか、設計空間の任意の場所を右クリックしてコンテキストメニューから Update Selected Part コマンドを選択します(ショートカット:
Ctrl+U)。これにより、アクティブなマルチボード・アセンブリ内の選択した部品が、対応する子 PCB ドキュメントの最新レイアウト情報で更新されます。 -
必要な 3D ボディを選択し、メインメニューから Edit » Update Selected 3D Body コマンドを選ぶか、デザインスペース内の任意の場所を右クリックしてコンテキストメニューから Update Selected 3D Body コマンドを選択します。これにより、アクティブなマルチボードアセンブリ内で選択した 3D ボディが、対応する子 PCB ドキュメントの最新レイアウト情報で更新されます。
パーツの編集
アセンブリまたは PCB の編集セッションは、マルチボードアセンブリエディタ内から起動できます。必要なパーツを選択して Edit » Edit Selected Part コマンドを実行するか、デザインスペース内の任意の場所を右クリックしてコンテキストメニューから Edit Selected Part コマンド(ショートカット: Ctrl+E)を選択します。コマンドを起動するとパーツ編集モードに入り、選択した PCB が(可能な場合)メインデザインウィンドウに収まるようにズームされ、中央に配置されます。ボードはフルカラー表示のまま、他のすべてのボードはグレーアウト(読み取り専用)表示になります。
必要に応じて、手動配置や整列機能を使用してコンポーネントの配置を変更します。編集が完了したら、 Finish Part Editing コマンド(Ctrl+E)を使用します。デザインスペースの表示はアセンブリ内のすべてのボードが収まる表示に戻り、編集していたボードは選択されたままになります。
変更を一切反映せずに編集をキャンセルしたい場合は、 Cancel Part Editing コマンドを使用します。
マルチボードアセンブリのナビゲーションと管理
マルチボードアセンブリをナビゲートおよび管理するには、Multiboard Assembly パネルを使用できます。

このパネルには、アセンブリ構造全体を含む展開可能なツリービューが表示されます。内容は次のとおりです。
-
含まれるボード(PCB)およびマルチボードアセンブリ、ならびに各 PCB 内のコンポーネント、レイヤ、ネット
-
含まれている STEP モデル
-
含まれている他のマルチボードアセンブリ
-
アセンブリ内のオブジェクト間で作成されたメイト
マルチボードアセンブリ内要素のハイライト
Multiboard Assembly パネルにはハイライト機能があり、ツリーで選択したパーツがデザインスペースでハイライト表示されます。アセンブリツリーの上位レベルで行った選択については双方向のハイライトが行われます。たとえば、デザインスペースでトップレベルのオブジェクトを選択すると、それに応じてパネルエントリの選択状態も変化します。パネルからの選択は、論理的に可能なツリーのすべてのレベルでサポートされます。たとえば、個々のネットを選択するとボード全体でそのネットがハイライトされますが、個々の誘電体レイヤを選択してもそのレイヤはハイライトされません。パネル内での複数選択には、標準の Windows Shift+Click または Ctrl+Click ショートカットを使用できます。

デザインスペースで 3 枚のボードを選択すると、パネル内でもハイライト表示されます。
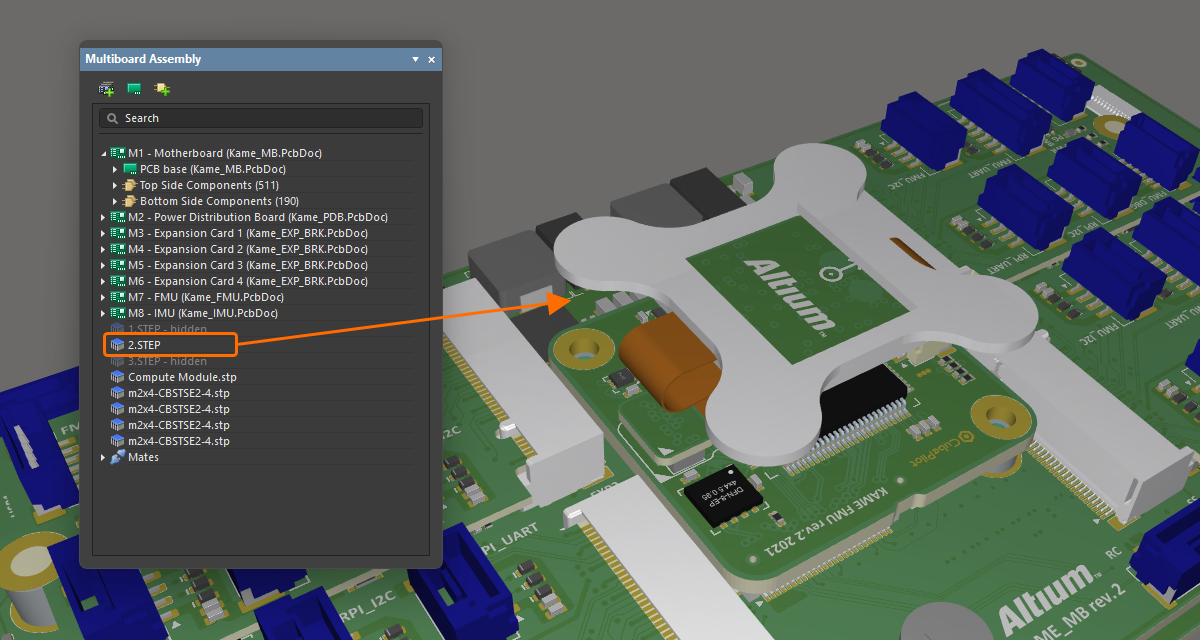
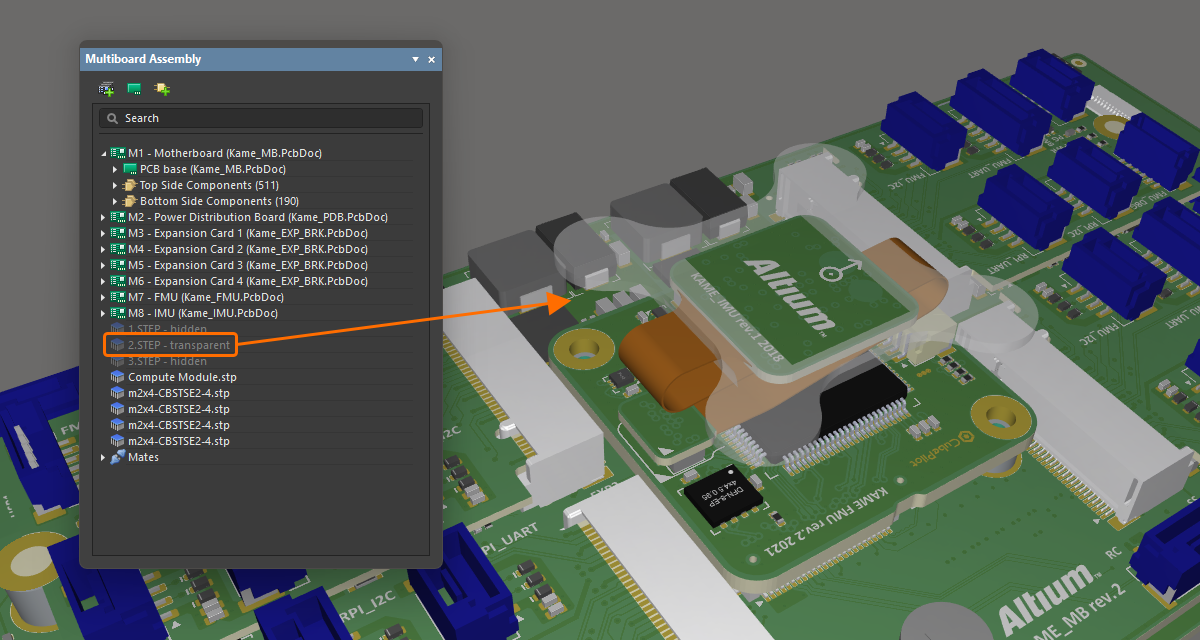
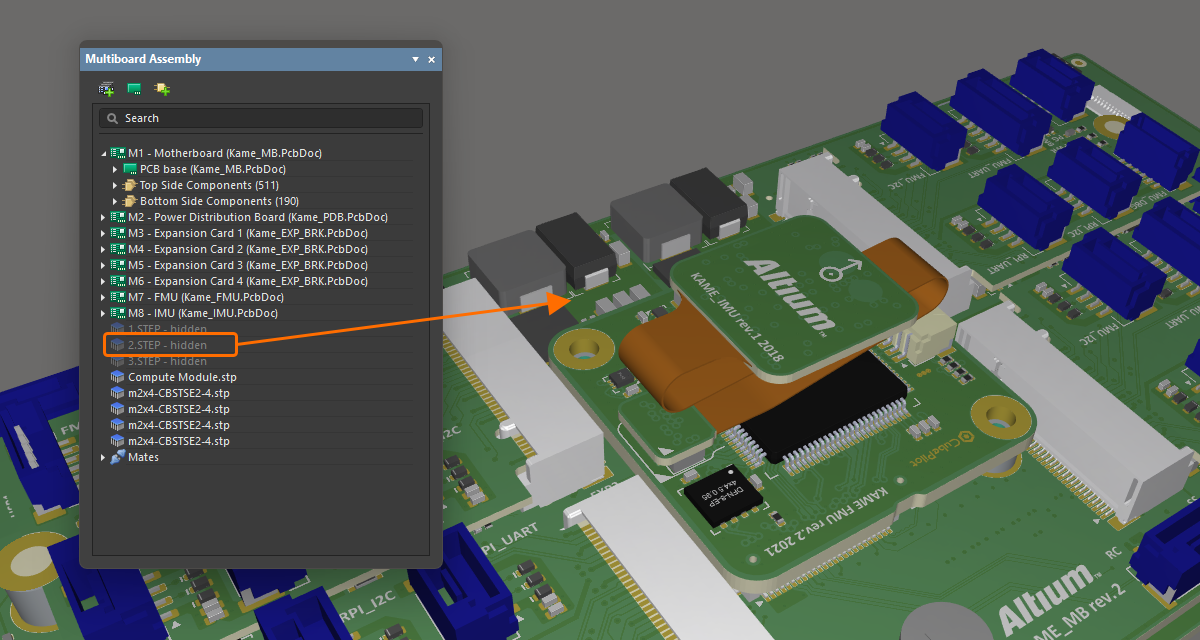
アセンブリパーツの表示/非表示と透明度の制御
特定のパーツ(複数可)をハイライトするだけでなく、パネルを使用して、パネル内で現在選択されているパーツの表示/非表示や透明度も制御できます。選択したパーツを右クリックし、コンテキストメニューから Visible または Transparent を選択します。透明にしたパーツは透けて表示されます。Visible オプションが無効になっているパーツは非表示になります。
|
STEP モデルがアセンブリ内で完全に表示されています。 同じモデルを透明にしました。 同じモデルを完全に非表示にしました。 |
距離の測定
メインメニューの Tools » Measure Distance コマンド(ショートカット: Ctrl+M)は、マルチボードアセンブリ内の 3D ボディ間の距離を測定するために使用します。コマンドを起動すると測定モードに入ります。測定は次の手順で行います。
-
最初の 3D オブジェクト、またはそのオブジェクトの特定の面を選択します。カーソルを候補の 3D オブジェクト上に移動すると、そのオブジェクトの色が変化します。オブジェクトの特定の面を選択したい場合は、カーソルを移動しながら
Ctrlキーを押し続けます。カーソル下の面がハイライトされます。カーソル位置を決めたらクリックして、オブジェクト/面の選択を確定します。 -
2 つ目の 3D オブジェクト、またはそのオブジェクトの特定の面を選択します。
-
ツールは、選択した 2 つのオブジェクト(面)間の最短距離を視覚的に表示します。
-
他のオブジェクト/面間の距離測定を続けるか、
Escを押して測定モードを終了します。
干渉チェック
2 つのオブジェクトの表面が接触または交差している場合、干渉としてフラグが立てられます。
干渉を確認するには、 Tools » Check Collisions (ショートカット: Ctrl+K)を選択します。コマンドを起動すると、ソフトウェアはマルチボードアセンブリに含まれる各エンティティ間の干渉をチェックします。まず各ボードについて、上側および下側の筐体/ケース部品(STEP 部品)との干渉をチェックし、その後、ボード同士(PCB 間)のチェックを行います。
干渉がある場合は Messages パネルに報告され、問題のオブジェクトは Violation システムカラーでハイライト表示されます。Messages パネルの Details 領域を使用して、衝突に関与しているボード上のどのコンポーネントが干渉の原因になっているかを調査できます。
必要に応じて、干渉チェック実行後にデザインスペースでハイライト表示されている干渉違反は、 Tools » Clear Violations コマンドを選択してクリアできます。
リジッドフレックスのサポート
マルチボードアセンブリエディタはリジッドフレックス PCB をサポートします。リジッドフレックスとは、フレキシブル回路とリジッド回路の両方を組み合わせたプリント回路の名称です。マルチボードアセンブリエディタでは、PCB エディタで定義された最終的な折り曲げ状態で PCB が表示されます。

リジッドフレックス PCB の設計については、 Designing a Rigid-Flex PCB ページを参照してください。
MCAD へのエクスポート
アセンブリは STEP 3D または Parasolid 形式でエクスポートできます。アセンブリ全体を STEP 3D(*.step または *.stp)でエクスポートするには、メインメニューから File » Export » STEP 3D を選択します。アセンブリ全体を Parasolid 形式(*.x_t)でエクスポートするには、メインメニューから File » Export » Parasolid を選択します。

MCAD ツールで開いたマルチボードアセンブリの STEP ファイルの例。
PDF 3D へのエクスポート
マルチボードアセンブリドキュメントは PDF ファイル(*.pdf)としてエクスポートすることもできます。これを行うには、メインメニューから File » Export to PDF File コマンドを選択します。

詳細は、Preparing a PDF3D File ページを参照してください。


 AI で翻訳
AI で翻訳