Определение конструкции устройства из нескольких электронных модулей
Altium Designer поддерживает создание многоплатной сборки, называемой multi-board assembly. После того как логическая структура системы определена в многоплатной схеме (*.MbsDoc), физический многоплатный дизайн создается путем переноса проекта системы в пустой документ многоплатной сборки (*.MbaDoc). В ходе этого процесса в редактор многоплатной сборки будут загружены физические представления (печатные платы и другие многоплатные сборки), на которые ссылается каждый логический блок в многоплатной схеме. На этой странице рассматривается данный процесс.
Чтобы узнать больше о логическом этапе проектирования многоплатной сборки, см. страницу Capturing the Logical System Design.
Чтобы создать новый документ многоплатной сборки:
-
Добавьте новый документ многоплатной сборки (
*.MbaDoc) в многоплатный проект, щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши по записи проекта в панели Projects, а затем выбрав Add New to Project » Multi-board Assembly в контекстном меню. -
Сохраните новый документ многоплатной сборки (щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по его записи в панели Projects и выберите Save As в контекстном меню).
-
Перенесите логическое представление системы из многоплатной схемы в документ многоплатной сборки – узнать больше.
-
Если корпус доступен, загрузите его в сборку – узнать больше.
-
Разместите каждый элемент внутри сборки – см. страницу Positioning & Orienting Your Boards, чтобы узнать больше.
-
Соедините элементы внутри сборки с помощью сопряжений (mates) – см. страницу Working with Mates, чтобы узнать больше.

Пример многоплатной сборки. Несколько соединенных печатных плат размещены внутри корпуса.
Перенос проекта системы в документ многоплатной сборки
Многоплатный дизайн переносится из многоплатной схемы в документ многоплатной сборки с помощью одной из следующих команд:
-
Design » Update Assembly - <MultiBoardAssemblyDocumentName>.MbaDoc из главного меню редактора многоплатной схемы.
-
Design » Import Changes From <MultiBoardProjectName>.PrjMbd из главного меню редактора многоплатной сборки.
При запуске одной из этих команд программа анализирует каждый модуль на многоплатной схеме, определяет PCB/сборку, выбранную для каждого дочернего проекта, и отображает список изменений, необходимых для добавления каждой из этих плат в сборку, в диалоговом окне Engineering Change Order.

Плата из каждого PCB‑проекта перечисляется как ECO‑изменение и загружается в редактор Multi-board Assembly при выполнении ECO.
Когда нажата кнопка ![]() , платы/сборки загружаются в редактор многоплатной сборки. Каждая плата/сборка размещается в рабочем пространстве в той же ориентации, что и в дочернем проекте. Этот процесс займет некоторое время, поскольку необходимо проанализировать и загрузить полный набор данных для каждой PCB.
, платы/сборки загружаются в редактор многоплатной сборки. Каждая плата/сборка размещается в рабочем пространстве в той же ориентации, что и в дочернем проекте. Этот процесс займет некоторое время, поскольку необходимо проанализировать и загрузить полный набор данных для каждой PCB.

Платы в этой многоплатной сборке загружены в рабочее пространство редактора многоплатной сборки и готовы к размещению.
Добавление дополнительных объектов в многоплатную сборку
Вы также можете загружать в многоплатную сборку дополнительные объекты (помимо PCB, на которые ссылается многоплатная схема). Дополнительные объекты можно загрузить через меню Design или с помощью кнопок, расположенных в верхней части панели Multi-board Assembly.

Используйте соответствующую команду или кнопку, чтобы:
-
Insert PCB Part – вставить в эту сборку еще одну PCB.
-
Insert MBA Part – вставить в эту сборку еще одну многоплатную сборку.
-
Insert STEP Part – вставить в эту сборку механическую модель в формате STEP.
Обновление или редактирование части сборки
Блокировка/разблокировка части
Чтобы заблокировать/разблокировать часть, выберите нужную часть, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши и затем выберите команду Lock Selected Part/Unlock Selected Part в контекстном меню, чтобы заблокировать/разблокировать часть (или сопряженные части) в ее текущем положении в рабочем пространстве редактора сборки. Либо щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по записи части в панели Multiboard Assembly, затем выберите Locked.
-
Заблокированную часть нельзя редактировать/перемещать.
-
Заблокированные части помечаются значком замка в панели Multiboard Assembly .
-
Для заблокированной отдельной части не отображается манипулятор объекта (gizmo) (подробнее о манипуляторе см. на странице Positioning & Orienting Your Boards).
-
Заблокированную часть нельзя сопрягать (mate), если она выбрана в качестве источника (объекта, который перемещается — подробнее о сопряжении частей см. на странице Working with Mates).
Обновление части
Если часть или 3D‑тело, добавленные в сборку, были обновлены, обновление можно загрузить в многоплатную сборку одним из следующих действий:
-
Выберите команду Edit » Update All Parts в главном меню или щелкните правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте рабочего пространства и выберите команду Update All Parts в контекстном меню (сочетание клавиш:
Shift+Ctrl+U), чтобы обновить все части в активной многоплатной сборке, загрузив актуальную информацию о разводке из соответствующих дочерних документов PCB. -
Выберите нужные части и выполните команду Edit » Update Selected Part в главном меню или щелкните правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте рабочего пространства и выберите команду Update Selected Part в контекстном меню (сочетание клавиш:
Ctrl+U) для обновления выбранных частей в активной многоплатной сборке с использованием актуальной информации о разводке из соответствующих дочерних документов PCB. -
Выберите требуемое 3D-тело и выполните команду Edit » Update Selected 3D Body в главном меню или щелкните правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте рабочей области и выберите команду Update Selected 3D Body в контекстном меню, чтобы обновить выбранные 3D-тела в активной многоплатной сборке с использованием актуальной информации о компоновке из соответствующих дочерних документов PCB.
Редактирование части
Сеанс редактирования сборки или PCB можно запустить прямо из редактора многоплатной сборки. Выберите нужную часть и выполните команду Edit » Edit Selected Part или щелкните правой кнопкой мыши в любом месте рабочей области и выберите команду Edit Selected Part в контекстном меню (сочетание клавиш: Ctrl+E). После запуска команды вы перейдете в режим редактирования части: выбранная плата будет масштабирована и, где возможно, отцентрирована так, чтобы поместиться в основном окне проектирования. Плата останется отображаться в полной цветовой схеме, а все остальные платы будут «приглушены» (только для чтения).
Внесите необходимые изменения в размещение компонентов, используя ручное размещение и/или функции выравнивания. Когда редактирование завершено, используйте команду Finish Part Editing (Ctrl+E). Вид рабочей области вернется к отображению всех плат в сборке, при этом плата, которая редактировалась, останется выделенной.
Если вы хотите отменить редактирование без применения каких-либо изменений, используйте команду Cancel Part Editing .
Навигация и управление многоплатной сборкой
Для навигации и управления многоплатной сборкой можно использовать панель Multiboard Assembly.

Панель отображает раскрываемое древовидное представление полной структуры сборки, включая:
-
Включенные платы (PCB) и многоплатные сборки и компоненты, слои и цепи (nets) внутри каждой PCB
-
Добавленные модели STEP
-
Другие включенные многоплатные сборки
-
Связи (mates), сформированные между объектами в сборке
Подсветка элементов в многоплатной сборке
Панель Multiboard Assembly предоставляет возможности подсветки: часть, выбранная в дереве, подсвечивается в рабочей области. Подсветка двунаправленная для выборов, сделанных на верхнем уровне дерева сборки; например, состояние выбора элементов панели будет меняться в ответ на выбор объектов верхнего уровня в рабочей области. На панели поддерживается выбор на всех уровнях дерева там, где это логично. Например, выбор отдельной цепи (net) подсветит эту цепь по всей плате, но выбор отдельного диэлектрического слоя не приведет к подсветке этого слоя. Для множественного выбора на панели можно использовать стандартные сочетания Windows Shift+Click или Ctrl+Click.

Три платы, выбранные в рабочей области, также подсвечиваются на панели.
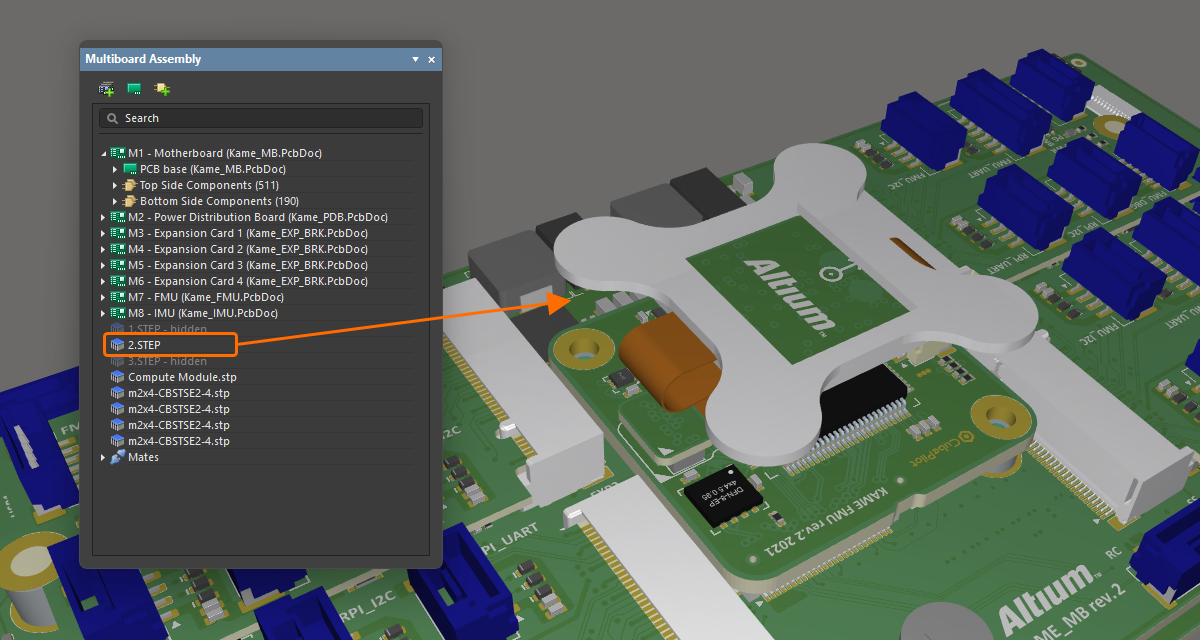
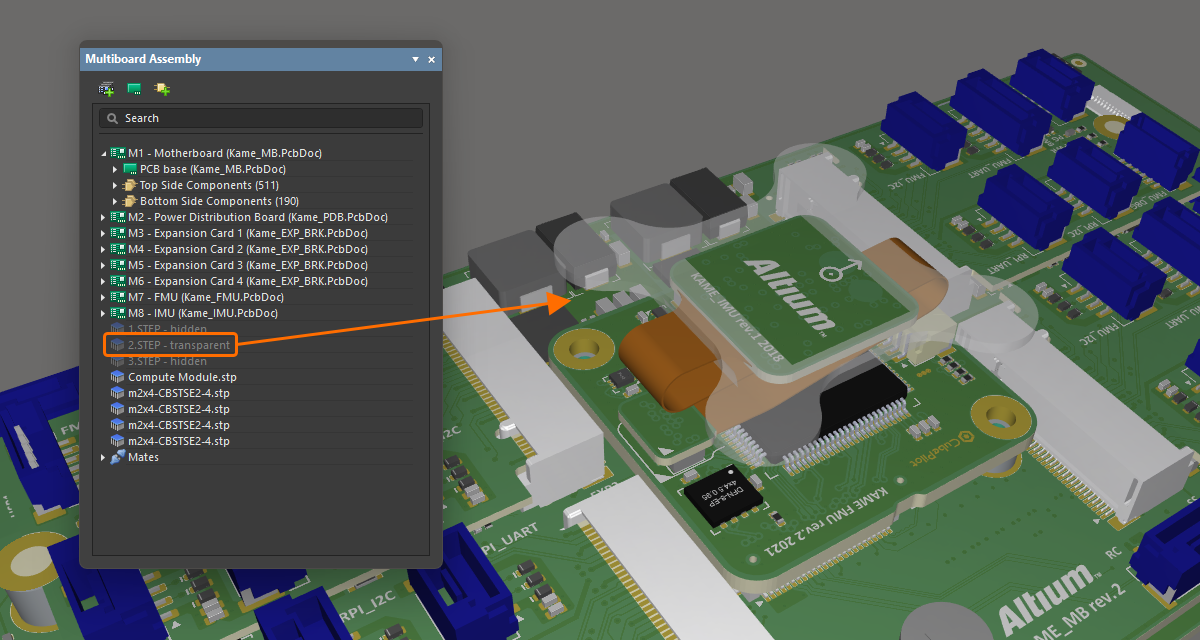
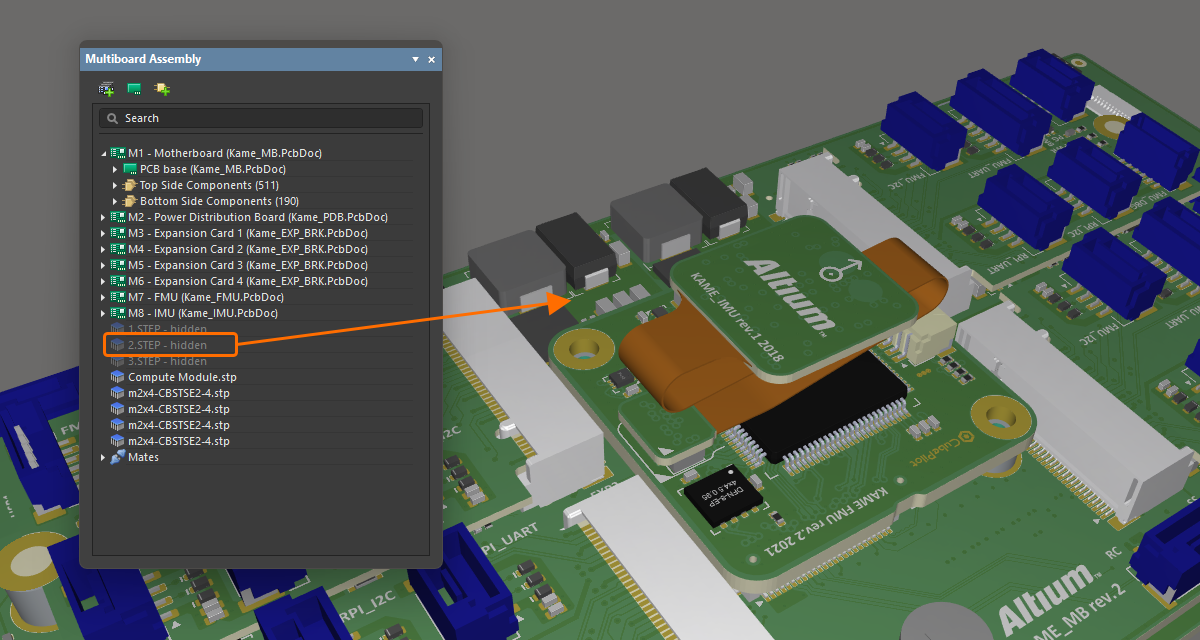
Управление видимостью и прозрачностью частей сборки
Помимо подсветки конкретной части или частей, панель также можно использовать для управления видимостью и прозрачностью частей, выбранных на панели. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по выбранной части(ям), затем выберите Visible или Transparent в контекстном меню. Прозрачные части станут полупрозрачными. Части, у которых отключена опция Visible , будут скрыты.
|
Модель STEP полностью видима в сборке. Та же модель сделана прозрачной. Та же модель полностью скрыта. |
Измерение расстояния
Команда Tools » Measure Distance в главном меню (сочетание клавиш: Ctrl+M) используется для измерения расстояний между 3D-телами в многоплатной сборке. После запуска команды вы перейдете в режим измерения. Измерение выполняется следующим образом:
-
Выберите первый 3D-объект или конкретную грань этого объекта. При перемещении курсора над потенциальным 3D-объектом цвет этого объекта будет изменяться. Если нужно выбрать конкретную грань объекта, удерживайте клавишу
Ctrlпри перемещении курсора — грань, находящаяся под курсором, будет подсвечиваться. Установив курсор, щелкните, чтобы подтвердить выбор объекта/грани. -
Выберите второй 3D-объект или конкретную грань этого объекта.
-
Инструмент визуально показывает кратчайшее расстояние между двумя выбранными объектами (гранями).
-
Продолжайте измерять расстояние между другими объектами/гранями или нажмите
Escдля выхода из режима измерения.
Проверка коллизий
Коллизии отмечаются всякий раз, когда поверхности двух объектов соприкасаются или пересекаются.
Чтобы проверить коллизии, выберите Tools » Check Collisions (сочетание клавиш: Ctrl+K). После запуска команды программа проверяет коллизии между различными сущностями, участвующими в многоплатной сборке. Сначала каждая плата проверяется на столкновение с верхними и нижними частями корпуса/кожуха (STEP-детали), затем выполняется проверка между самими платами (PCB).
Все коллизии будут отображены на панели Messages , а проблемные объекты будут подсвечены с использованием системного цвета Violation . Используйте область Details панели Messages , чтобы определить, какой компонент на плате, участвующей в конфликте, вызывает столкновение.
При необходимости нарушения коллизий, подсвеченные в рабочей области после выполнения проверки, можно очистить, выбрав команду Tools » Clear Violations .
Поддержка Rigid-Flex
Редактор многоплатной сборки поддерживает платы rigid-flex. Rigid-flex — это печатная плата, представляющая собой комбинацию гибких цепей и жестких участков. Редактор многоплатной сборки отображает PCB в конечном сложенном состоянии, определенном в редакторе PCB.

Сведения о проектировании плат rigid-flex см. на странице Designing a Rigid-Flex PCB.
Экспорт в MCAD
Сборку можно экспортировать в формат STEP 3D или Parasolid. Чтобы экспортировать всю сборку в STEP 3D (*.step или *.stp), выберите File » Export » STEP 3D в главном меню. Чтобы экспортировать всю сборку в формате Parasolid (*.x_t), выберите File » Export » Parasolid в главном меню.

Пример STEP-файла многоплатной сборки, открытого в MCAD-инструменте.
Экспорт в PDF 3D
Документ многоплатной сборки также можно экспортировать в PDF-файл (*.pdf). Для этого выберите команду File » Export to PDF File в главном меню.

Дополнительные сведения см. на странице Preparing a PDF3D File.


 Локализовано с помощью ИИ
Локализовано с помощью ИИ