Библиотеки компонентов на основе базы данных, которые получают параметры компонентов из основной (master) базы данных, можно синхронизировать с этой базой данных после миграции библиотеки в Altium 365 Workspace или Enterprise Server Workspace.
Используя функцию Components Synchronization в Altium Designer, как описано ниже, данные из выбранной таблицы в основной базе данных используются для создания полностью настроенного и сопоставленного профиля синхронизации, который можно запускать по требованию или по расписанию. В результате обновления данных в основной базе будут распространяться на соответствующие параметры компонентов в подключенном Workspace.
Функция позволяет компаниям, которые централизованно управляют данными компонентов в базе данных корпоративной системы, использовать преимущества Workspace, сохраняя синхронизацию со своей корпоративной системой (PLM, PDM, ERP и т. п.) — либо просто с общей базой данных или CSV‑файлом. В режиме автосинхронизации планировщик задач Windows будет выполнять обновление данных из базы данных в Workspace независимо от клиентского приложения Altium Designer.
См. Importing Existing Libraries to Your Connected Workspace для получения информации об импорте библиотек баз данных в ваш Workspace.
Чтобы получить доступ к возможностям синхронизации компонентов в Altium Designer, для вашей установки Altium Designer должна быть включена функция Custom Data Synchronization. Эту функцию можно включать/отключать после установки.
Дополнительные сведения об изменении установленной базовой функциональности см. на странице Installing & Managing (Altium Designer Develop, Altium Designer Agile, Altium Designer).
Создание конфигурации синхронизации компонентов
Синхронизация «база данных → Workspace» настраивается путем создания и настройки документа Components Synchronization Configuration (*.CmpSync) в Altium Designer. При подключении к вашему Workspace создайте новый документ с помощью команды меню File » New » Components Synchronization Configuration.
Добавьте нужный основной источник данных в конфигурацию синхронизации с помощью кнопки  или перетащив подходящие файлы в область Data Sources интерфейса. Конфигурация поддерживает следующие источники данных параметров компонентов:
или перетащив подходящие файлы в область Data Sources интерфейса. Конфигурация поддерживает следующие источники данных параметров компонентов:
-
Файлы Database Library (*.dBLib) — которые ссылаются на основной источник базы данных.
-
Файлы баз данных Access (*.mdb, *.accdb)
-
Таблицы Excel (*.xlsx)
-
CSV‑файлы (*.csv)
-
Другие источники данных, например серверные интерфейсы, совместимые с OLE DB, через проприетарную строку подключения.
В приведенном ниже примере в конфигурацию добавлена библиотека базы данных для компонентов Zener диодов — обратите внимание, что эта dBLib ранее была мигрирована в Workspace. Исходная база данных библиотеки (Semi_8.mdb) содержит таблицы DiodeGP и Zeners, при этом последняя таблица включена для синхронизации.
Выберите таблицу (или таблицы) данных для синхронизации на панели Properties panel, после чего она используется как параметрический источник данных, заполняющий список Components Preview. Система попытается определить тип компонента (резистор, конденсатор и т. п.) по данным параметров, а затем применить к конфигурации этот Component Type и соответствующий ему Component Template — при необходимости эти настройки можно выбрать вручную. Выберите запись таблицы в разделе Data Sources, чтобы увидеть текущую конфигурацию на панели Properties.

В этом примере тип компонента (Zeners) был определен, и применен его Component Template. Шаблон затем определяет целевую папку Workspace, схему именования компонентов и применяемое определение жизненного цикла. Записи компонентов сопоставляются с исходными записями базы данных по уникальному идентификатору, заданному параметром Key Parameter на панели Properties — в данном случае используется Part Number, хотя Name или даже Description были бы столь же эффективны.
Когда в качестве источника данных используется Database Library (*.dBLib), а не прямой источник типа базы данных (*.mdb, *.xlsx и т. п.), из файла dBLib извлекается и применяется к конфигурации следующая информация:
-
Подключение к исходной базе данных и путь.
-
Выбор таблицы базы данных.
-
Ключевое поле поиска (параметр).
Таким образом, эти настройки конфигурации будут соответствовать тем, что использовались при создании dBLib, обеспечивая корректную синхронизацию между мигрированными компонентами dBLib и исходной базой данных.
Синхронизация
Когда настройка синхронизации вас устраивает, сохраните документ конфигурации и выполните синхронизацию компонентов библиотеки из базы данных в Workspace с помощью кнопки  либо настройте синхронизацию по расписанию (
либо настройте синхронизацию по расписанию ( ).
).
В показанном ниже примере параметр описания для двух записей компонентов был обновлен в исходной/основной базе данных. Эти изменения можно увидеть, нажав кнопку обновления ( ) в интерфейсе конфигурации — это необязательно и не влияет на синхронизацию обновленных данных.
) в интерфейсе конфигурации — это необязательно и не влияет на синхронизацию обновленных данных.

Последующая синхронизация обновит параметры компонентов в Workspace на основе текущих данных полей базы данных. Это изменение можно увидеть на панелях Components и Explorer. Обновите их представления с помощью клавиши F5 или кнопки  соответственно.
соответственно.
Подробные файлы журнала синхронизации доступны в системной папке C:\Users\Public\Documents\Altium\Logs\ComponentSync.
Как видно на панели Explorer, для двух обновленных компонентов были созданы новые ревизии. Какие параметры будут создавать новые ревизии компонента при обновлении из основной базы данных, определяется настройками Parameter Mapping в конфигурации синхронизации.

Ревизии Component Item, созданные в процессе синхронизации компонентов, будут иметь примечание Created by component synchronization или Modified by component synchronization (в зависимости от того, был ли создан новый элемент или новая ревизия существующего элемента). Отобразите столбец Note для просматриваемого типа компонентов на панели Components или для просматриваемой папки Workspace на панели Explorer, чтобы легко идентифицировать компоненты, созданные/измененные синхронизацией компонентов.
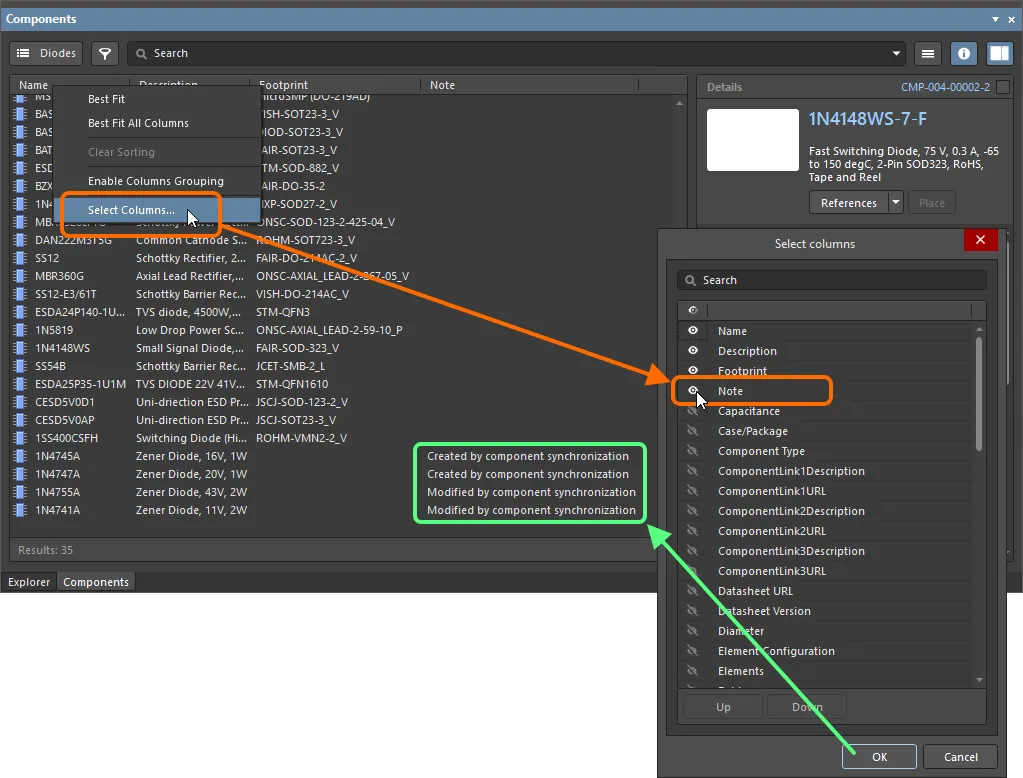
Отобразите столбец Note при просмотре компонентов. Здесь показан пример на панели Components. Наведите курсор на изображение, чтобы увидеть панель Explorer.
Сопоставление параметров
Управление синхронизируемыми параметрами доступно в области Parameter Mapping панели Properties, где представлена таблица соответствий между целевыми параметрами Workspace и параметрами (полями) исходной базы данных. Также доступны настройки типа передаваемого параметра (текстовый или с учетом единиц измерения) и управление созданием новой ревизии при обновлении параметров.
С точки зрения сопоставления параметров, столбцы таблицы представляют целевой объект Workspace (Parameter) и поля исходной/основной базы данных (Column) — как в данных столбцов, показанных в таблице Components Review основного интерфейса конфигурации. Параметры можно исключать из синхронизации (пропускать) или переназначать на другой доступный параметр. Имена параметров можно редактировать, а наборы параметров — добавлять, изменять и удалять. Базовые параметры компонента (ID, Name, Description) можно переназначать, но в остальном они доступны только для чтения.

На изображении выше показаны три состояния сопоставления параметров на панели Properties. Слева — когда Component Template не применен, центральное изображение — результат после указания шаблона, а изображение справа демонстрирует измененное сопоставление параметров и управление ревизиями.
-
Левое изображение: По умолчанию, без примененного шаблона, параметры по сути сопоставляются по принципу «один к одному» между основной базой данных и компонентами Workspace. Набор параметров ID, установленный в <Auto> здесь, представляет автоматическое создание (при необходимости) параметра Workspace Revision ID, который связан с текущей настройкой Item Revision Naming Scheme — в разделе Advanced на панели. Также обратите внимание, что поле базы данных Comment автоматически сопоставляется с параметром Workspace Name.
-
Центральное изображение: Когда применяется Component Template (Zeners здесь), поля параметров базы данных сопоставляются с эквивалентными параметрами шаблона. Система автоматически интерпретирует распространенные сопоставления параметров, например Pin Count с Pins (параметр шаблона) в данном случае. Параметры, не определенные в шаблоне, сопоставляются по принципу «один к одному» — девять параметров внизу списка в этом примере.
-
Правое изображение: Ряд параметров базы данных был исключен из конфигурации синхронизации путем установки режима их столбцов в <Skip>. Параметр PackageReference был сопоставлен с полем основной базы данных Footprint. Для параметров Revision снят флажок у параметров VZ(Max), VZ(Min) и ZZ(Max), что означает: изменение их значения в основной базе данных не приведет к созданию новой ревизии в Workspace при синхронизации — однако измененное значение, как обычно, будет передано в компонент Workspace.
Сопоставление выбора компонента
Используя документ конфигурации синхронизации компонентов, вы можете задавать и синхронизировать информацию о выборе детали (part choice). Управление синхронизируемыми параметрами доступно в области Part Choices Mapping панели Properties. Используйте кнопки в нижней части области, чтобы добавлять и удалять пары параметров выбора детали (Manufacturer / Part Number), а также параметры выпадающих меню для задания сопоставления. Когда сопоставления определены, соответствующие параметры появляются под столбцами Part Choice n в области сетки документа.

Обратите внимание: после выполнения процесса синхронизации список выбора детали (part choice) компонента будет перезаписан заново сопоставленными вариантами, за исключением тех вариантов, которые были добавлены вручную.
Панель Properties
Когда активным документом является документ конфигурации синхронизации компонентов (*.CmpSync), панель Properties отображает параметры конфигурации. Следующие сворачиваемые разделы содержат сведения о доступных параметрах и элементах управления.
Component Type Table

На изображении выше показаны три состояния сопоставления параметров на панели Properties. Слева — когда шаблон компонента (Component Template) не применён, центральное изображение — результат после указания шаблона, а изображение справа демонстрирует изменённое сопоставление параметров и управление Revision.
-
Reset to Default – используется для отмены всех внесённых изменений.
-
General
-
Component Type – отображает определённый тип компонента.
-
Component Template – отображает определённый шаблон компонента, который задаёт целевую папку Workspace, схему именования компонента (Naming Scheme) и применяемое определение жизненного цикла (Lifecycle).
-
Key Parameter – отображает ключевой параметр, сопоставленный с записью исходной базы данных с использованием уникального идентификатора.
-
Advanced
-
Folder – целевая папка Workspace, в которой находится компонент.
-
Revision Naming Scheme – схема именования, используемая для ревизий объекта в Workspace, заданная применённым шаблоном или выбранная из вариантов выпадающего меню записи. В качестве вариантов будут доступны только те схемы, которые включены в системе.
-
Lifecycle Definition – система Lifecycle system, используемая для объекта, заданная применённым шаблоном или выбранная из вариантов выпадающего меню записи. В качестве вариантов будут доступны только те определения, которые включены в системе.
-
Preserve lifecycle state – включите этот параметр, чтобы сохранять текущие состояния жизненного цикла ревизий компонентов. Когда параметр включён, новые ревизии компонентов, создаваемые при выполнении синхронизации компонентов, будут автоматически устанавливаться в состояние жизненного цикла предыдущей ревизии. Эта возможность доступна пользователям с назначенным операционным разрешением Allow to skip lifecycle state change for new revisions (подробнее см. Setting Global Operation Permissions for a Workspace).
-
Parameter Mapping – предоставляет таблицу, показывающую взаимосвязь между целевыми параметрами Workspace и параметрами (полями) исходной базы данных. Также доступны настройки передаваемого параметра Type (текстовый или с учётом единиц измерения) и управление созданием новой Revision при обновлении параметров. В части сопоставления параметров столбцы таблицы представляют целевой объект Workspace (Parameter) и поля исходной/мастер-базы данных (Column).
-
Part Choices Mapping – предоставляет элементы управления, с помощью которых можно задавать пары параметров выбора детали (Manufacturer / Part Number) для синхронизируемой информации о выборе детали. Используйте параметры выпадающих меню, чтобы определить сопоставление.
Table Inclusion

Table Inclusion – отображает включение таблиц базы данных, которые можно отметить для синхронизации на панели Properties; затем они используются как параметрический источник данных, заполняющий список Components Preview в меню Component Synchronization Configuration.
Плановая синхронизация
Сохранённые конфигурации синхронизации настраиваются для автоматизированной обработки компонентов из базы данных в Workspace через диалог Auto Synchronization Schedule, открываемый кнопкой  в основном интерфейсе.
в основном интерфейсе.
Плановую синхронизацию, в соответствии с текущим профилем конфигурации, можно настроить на определённое время каждый день, на конкретное время в разные дни недели или на момент входа в Windows. Также можно отключить синхронизацию на время, когда вы не вошли в систему. Когда вы подтверждаете настройки кнопкой  , конфигурация будет добавлена как повторяющаяся задача в Windows Task Scheduler. Установите значение No automatic synchronization, чтобы удалить существующее расписание синхронизации.
, конфигурация будет добавлена как повторяющаяся задача в Windows Task Scheduler. Установите значение No automatic synchronization, чтобы удалить существующее расписание синхронизации.

Синхронизацию «база данных → компоненты» также можно запускать из командной строки с помощью приложения ComponentSync.Executor.exe, находящегося в папке установки ПО \System. Синтаксис команды: ComponentSync.Executor.exe [configuration file name]. Типичный пример может быть таким:
C:\Program Files\Altium\AD<Solution/Version>\System\ComponentSync.Executor.exe C:\Users\Public\Documents\Altium\CmpSync\MySyncConfig.CmpSync

В зависимости от операционной системы для путей, содержащих пробелы, может потребоваться заключать их в кавычки.