Разметка печатной платы
Altium Essentials: PCB Introduction
This content is part of the official Altium Professional Training Program. For full courses, materials and certification, visit Altium Training.
Внутри каждого электронного изделия находится печатная плата (PCB). Сегодня компоненты настолько уменьшились, что их размеры измеряются долями миллиметра, а не сантиметрами, а ширина дорожек сократилась с 10 mil — широких, хорошо разнесённых линий — до тонких, «волосовидных» линий 2–3 mil, плотно расположенных друг к другу. Рост скоростей сигналов также привёл к тому, что межсоединения на PCB изменились: из простых медных проводников, переносящих электрическую энергию, они превратились в высокоскоростные линии передачи, что требует соответствующих методик проектирования. Механические требования тоже усложнились. Компактные современные электронные изделия необычной формы требуют компактных печатных плат необычной формы, которые часто выполняются как rigid-flex конструкции — такие платы могут иметь криволинейные края и вырезы, что требует тщательно выверенного размещения компонентов.
Эти задачи можно решить с помощью технологий проектирования PCB от Altium. PCB-редактор Altium Designer позволяет создавать, редактировать и проверять проекты печатных плат.
Настройка PCB-редактора
Категория PCB Editor в диалоговом окне Preferences (открывается нажатием значка ![]() в правом верхнем углу рабочей области) предоставляет доступ к страницам настроек, влияющих на поведение PCB-редактора. К этим настройкам можно обращаться в любой момент, чтобы при необходимости сконфигурировать параметры.
в правом верхнем углу рабочей области) предоставляет доступ к страницам настроек, влияющих на поведение PCB-редактора. К этим настройкам можно обращаться в любой момент, чтобы при необходимости сконфигурировать параметры.

Используйте категорию PCB Editor в Preferences Altium Designer для настройки PCB-редактора.
Подробнее о настройках PCB: PCB Editor Preferences.
Создание PCB-документа
Чтобы начать трассировку и компоновку платы, добавьте новый PCB-документ в PCB-проект. Для этого щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши по записи проекта в панели Projects и выберите команду Add New to Project » PCB в контекстном меню. В рабочей области появится PCB-документ по умолчанию.

Вновь созданный PCB-документ станет активным документом в рабочей области.
Параметры PCB-документа настраиваются в панели Properties, когда в рабочей области не выбран ни один объект. Основные параметры задаются на вкладке General этой панели:
-
Настройка сетки (область Grid Manager) — настройте параметры глобальной сетки по умолчанию или при необходимости добавьте дополнительные сетки (декартовы и полярные). Сетки обеспечивают точное перемещение и размещение объектов.
- Единицы (область Other) — выберите предпочтительные единицы измерения (mm или mils) для документа.

Настройте параметры PCB-документа в панели Properties.
Подробнее о настройке PCB-документа: PCB Environment Setup.
Определение контура платы и начала координат
Контур платы (board shape), также называемый board outline, задаёт общие габариты платы. По умолчанию плата представляет собой прямоугольник 6000 x 4000 mil (152,4 x 101,6 мм). PCB-редактор предоставляет ряд инструментов для задания контура платы в соответствии с требованиями.
Вы можете интерактивно задать новый контур платы следующим образом:
-
Перейдите в режим планирования платы (Board Planning Mode), выбрав в главном меню команду View » Board Planning Mode .
-
Выберите в главном меню команду Design » Redefine Board Shape .
-
Расположите курсор и щёлкните, чтобы зафиксировать начальную вершину контура платы.
-
Переместите курсор к месту второй вершины и щёлкните, чтобы установить её.
-
Продолжайте перемещать мышь и щёлкать, чтобы задавать последующие вершины.
-
После установки последней вершины щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы замкнуть и завершить определение контура платы. Вручную замыкать контур не требуется — PCB-редактор автоматически завершит фигуру, соединив начальную точку с последней установленной точкой.
Вы также можете отредактировать существующий контур вместо его переопределения, используя следующий процесс:
- Перейдите в режим планирования платы (Board Planning Mode), выбрав в главном меню команду View » Board Planning Mode .
- Выберите в главном меню команду Design » Edit Board Shape.
-
Щёлкните, удерживайте и перетащите сторону или вершину контура платы, чтобы переместить её.
- Выйдите из режима редактирования, щёлкнув в любом месте рабочей области (на контуре платы или вне его).
Используйте команду View » 2D Layout Mode в главном меню, чтобы вернуться в режим 2D Layout Mode.
Подробнее о доступных методах задания контура платы: Defining the Board Shape.
Настройка отображения слоёв
Помимо слоёв, используемых для изготовления платы (включая сигнальные слои, слои внутренних плоскостей питания, маску и шелкографию), PCB-редактор также поддерживает множество других неэлектрических слоёв. Слои часто группируются следующим образом:
-
Electrical Layers — включает 32 сигнальных слоя и 16 внутренних слоёв плоскостей питания.
-
Component Layers — слои, используемые при проектировании компонентов, включая Overlay (шелкография), Solder и Paste. Если объект размещён в посадочном месте компонента на одном из этих слоёв в редакторе библиотек, то при перевороте компонента с верхней стороны платы на нижнюю все объекты, обнаруженные на слое Component, переворачиваются на парный слой Component. Это также относится к объектам на пользовательских парах слоёв Component Layer Pairs (спаренных механических слоях).
-
Mechanical Layers — программное обеспечение поддерживает неограниченное количество механических слоёв общего назначения, которые используются для таких задач, как размеры, данные для производства, инструкции по сборке и т. п. При необходимости эти слои можно выборочно включать в печать и генерацию Gerber-выходных данных. Механические слои также могут быть спарены; в этом случае они ведут себя как слои Component Layers. Спаренные Component Layers применяются для таких задач, как размещение 3D-тел, точки клея и выборочное золочение на краевых разъёмах.
-
Other Layers — сюда входят слой Keep-Out (используется для задания запретных областей, действующих на всех медных слоях), слой multi-layer (для объектов, присутствующих на всех сигнальных слоях, например площадок и переходных отверстий), слой Drill Drawing (для размещения информации о сверлении, например таблицы сверловки) и слой Drill Guide (для отображения маркеров, указывающих места и размеры сверления).
Медные слои добавляются и удаляются из проекта в Layer Stack Manager, который рассматривается в следующем разделе. Все остальные слои включаются и настраиваются в панели View Configuration.


Две вкладки панели View Configuration
Помимо состояния отображения слоёв и настроек цветов, панель View Configuration также предоставляет доступ к другим параметрам отображения, включая:
-
Цвет и видимость System Colors, например цвет выделения (Selection) или отображаются ли линии соединений (Connection Lines).
-
Как отображается каждый тип объекта (сплошной или черновой), а также его прозрачность (раздел Object Visibility).
-
Различные параметры вида, например нужно ли отображать названия Origin Marker, Pad Net и Pad Numbers (раздел Additional Options).
-
Степень «приглушения» отображения при затемнении или маскировании объектов (раздел Mask and Dim Settings).
-
Создание наборов слоёв (Layer Sets), которые позволяют быстро переключать, какие слои сейчас видимы, с помощью элемента управления
 (раздел Layers).
(раздел Layers).
-
Создание и выбор конфигураций вида (View Configurations), которые используются для предварительной настройки всех свойств слоёв — цвета, видимости, прозрачности объектов и т. п. (раздел General Settings).
Некоторые примечания о слоях:
-
Текущие включенные слои отображаются в виде ряда вкладок внизу рабочей области проектирования PCB, как показано на изображении ниже. Щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по вкладке, чтобы получить доступ к часто используемым командам отображения слоев.
-
При размещении объектов на PCB следует учитывать, на каком слое они будут размещены. Объекты размещаются на текущем слое, который показан как активная вкладка слоя внизу рабочей области. На изображении выше активным слоем является Top Layer.
-
Чтобы переключить активный слой:
-
Щелкните вкладку слоя внизу рабочей области, или
-
Нажимайте цифровые клавиши + или -, чтобы циклически переключаться по всем слоям, или
-
Нажимайте цифровую клавишу *, чтобы циклически переключаться по сигнальным слоям, или
-
Используйте сочетания клавиш Ctrl+Shift+Mouse Wheel.
-
-
В загруженном проекте может быть полезно отображать только слой, над которым вы сейчас работаете; это называется Single Layer Mode. Чтобы включать/выключать режим одного слоя, нажмите сочетание клавиш Shift+S. Режимы Available Single Layer Modes настраиваются на странице PCB Editor – Board Insight Display диалога Preferences. Каждое нажатие Shift+S будет переключать на следующий включенный режим одного слоя.
Подробнее о настройке вида PCB: Your View of the PCB.
Определение стека слоев
Плата PCB проектируется и формируется как стек слоев, определяемый в Layer Stack Manager (Design » Layer Stack Manager). Layer Stack Manager открывается в редакторе документов так же, как лист схемы, PCB и другие типы документов. Функциональность разделена по вкладкам, расположенным внизу Layer Stack Manager. Основные операции конфигурирования выполняются на вкладках Stackup и Via Types .
Вкладка Stackup содержит сведения о производственных слоях. На этой вкладке слои добавляются, удаляются и настраиваются.
|
Чтобы добавить слой, выберите в области таблицы слой, выше/ниже которого нужно добавить новый слой, и нажмите кнопку Add в верхней части Layer Stack Manager , затем воспользуйтесь появившимся всплывающим окном. Чтобы удалить слой, выберите его в области таблицы и нажмите кнопку Delete. Чтобы выбрать материал слоя из библиотеки материалов, выделите нужный слой в области таблицы и нажмите кнопку Modify. Свойства, заданные для выбранного материала, будут применены к слою. Свойства текущего выбранного слоя также можно редактировать напрямую в области таблицы или на панели Properties . |
Вкладка Via Types используется для задания допустимых требований по Z-оси (по слоям), которые определяют, какие слои могут соединять переходные отверстия (via), используемые в проекте.
|
Тип переходного отверстия по умолчанию (сквозное) всегда присутствует в проекте PCB. Чтобы добавить дополнительный тип via (blind, buried или micro via), нажмите кнопку Add в верхней части Layer Stack Manager , затем выберите слои, которые охватывает этот тип via, в выпадающих списках First layer и Last layer на панели Properties, когда тип via выбран в области таблицы. Чтобы удалить добавленный тип via, выберите его в области таблицы и нажмите кнопку Delete . |
Используйте команду File » Save to PCB в Layer Stack Manager , чтобы отразить изменения в PCB.
Подробнее о Layer Stack Manager: Defining the Layer Stack, Blind, Buried & Micro Via Definition.
Настройка правил проектирования
Правила проектирования контролируют и проверяют ваш проект на соответствие различным требованиям, таким как зазоры между медными объектами, ширины трасс, длины цепей и т. п. В совокупности правила проектирования образуют набор инструкций, которым должен следовать редактор PCB.
Правила проектирования задаются и управляются из диалога PCB Rules and Constraints Editor , который открывается выбором команды Design » Rules в главном меню.
Диалог PCB Rules and Constraints Editor содержит два раздела:
- В левой части диалога отображается дерево, в котором перечислены доступные категории правил, типы правил в каждой категории, а также отдельные правила каждого типа, которые в данный момент определены.
- В правой части диалога отображается информация, относящаяся к тому, что сейчас выбрано в дереве. Например, выберите отдельное правило, чтобы увидеть его настройки.
У правил проектирования есть три группы настроек, описанные ниже и показанные на изображениях далее:
- Основные атрибуты правила — здесь можно задать правилу понятное имя и добавить необязательный комментарий.
- Область действия правила — определяет конкретные объекты в проекте, на которые нацелено правило. В зависимости от типа правила следует задать одну область (для унарного правила, определяющего требуемое поведение объекта) или две (для бинарного правила, определяющего взаимодействие между двумя объектами).
- Ограничения правила — конкретные ограничения для правила.
|
Правила типа Width являются унарными. Для унарного правила следует определить одну область (Where the Object Matches). Правила типа Clearance являются бинарными. Для бинарного правила следует определить две области (Where the First Object Matches и Where the Second Object Matches). |
Чтобы создать новое правило, щелкните правой кнопкой мыши по нужному типу правила в дереве диалога и выберите команду New Rule в контекстном меню. Новое правило будет добавлено в дерево в выбранной категории. Выберите элемент правила в дереве, чтобы отредактировать его.
Когда существует несколько правил одного типа, нацеленных на один и тот же объект (или объекты), редактор PCB использует приоритет правил, чтобы применялось подходящее правило с наивысшим приоритетом. Нажмите кнопку Priorities внизу диалога PCB Rules and Constraints Editor , чтобы открыть диалог Edit Rule Priorities и при необходимости изменить приоритеты. 1 — наивысший приоритет. Когда добавляется новое правило (командой New Rule), ему назначается наивысший приоритет.
Подробнее о работе с правилами проектирования PCB и конкретными типами правил: Defining, Scoping & Managing PCB Design Rules, PCB Design Rule Types.
Размещение компонентов
Когда данные проекта переносятся со схем проекта PCB в документ PCB (с помощью команды Design » Update PCB Document в главном меню редактора схем и последующего процесса выполнения ECO), посадочные места компонентов, используемых на схемах, будут размещены в произвольных позициях в документе PCB. Контактные площадки компонентов будут соединены линиями соединений в соответствии с цепями (соединенными выводами компонентов), определенными на схемах.

PCB после обновления по данным схем.
Основные приемы задания положения компонента на PCB:
- Чтобы переместить компонент в нужное место, Click, Hold&Drag , затем отпустите кнопку мыши, чтобы разместить его.
- Чтобы повернуть компонент, нажмите Spacebar во время перетаскивания.
- Чтобы перевернуть компонент на другую сторону платы, нажмите L во время перетаскивания.
Линии соединений автоматически переоптимизируются при перемещении компонента. Используйте их, чтобы ориентировать и располагать компоненты так, чтобы уменьшить количество пересечений линий соединений.
Узнайте больше о связности на PCB и размещении компонентов: Понимание связности на вашей PCB, Размещение компонентов.
Трассировка платы
Трассировка — это процесс прокладки дорожек, дуг и переходных отверстий (via) на плате для соединения контактных площадок компонентов. Редактор PCB предлагает инструменты, включая интерактивные средства трассировки, чтобы помочь с прокладкой соединений на вашей плате.
Поскольку инструменты трассировки управляются правилами, крайне важно настроить правила проектирования до начала трассировки. Основные правила проектирования, используемые в процессе интерактивной трассировки:
- Правило Clearance (категория Electrical) – определяет, насколько близко трассы прокладываемой цепи (net) могут подходить к другим объектам на плате.
- Правило Width (категория Routing) – определяет ширину трасс для прокладываемой цепи.
- Правило Routing Via Style (категория Routing) – определяет диаметр и размер отверстия переходных отверстий, устанавливаемых при переключении слоёв во время трассировки.
Также рекомендуется установить snap-сетку, подходящую для трассировки.
Чтобы проложить одно соединение, используется инструмент Interactive Routing. Процесс следующий:
-
Выберите команду Route » Interactive Routing в главном меню.
-
Щёлкните по контактной площадке компонента, от которой вы хотите начать трассировку.
-
Расположите курсор, затем щёлкните в рабочей области, чтобы разместить дорожки до курсора. Продолжайте задавать путь трассы.
-
Щёлкните по целевой площадке, чтобы завершить трассировку соединения. Соединение будет автоматически отпущено, и вы останетесь в режиме интерактивной трассировки, готовые прокладывать следующее соединение.
-
Щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы выйти из режима интерактивной трассировки.
Примечания по интерактивной трассировке:
-
При подведении курсора близко к площадке во время интерактивной трассировки он автоматически «прилипает» к центру площадки. Это функция hotspot объекта, притягивающая курсор к hotspot ближайшего электрического объекта.
Узнайте больше о работе с системой прилипания курсора.
-
Во время интерактивной трассировки можно использовать следующие сочетания клавиш:
-
Tab — чтобы приостановить трассировку и открыть панель Properties для настройки параметров интерактивной трассировки. По завершении нажмите кнопку
 в рабочей области, чтобы вернуться в режим интерактивной трассировки.
в рабочей области, чтобы вернуться в режим интерактивной трассировки.
-
Shift+Spacebar — чтобы циклически переключать стили углов: Track 45, Line 45/90 With Arc, Any Angle и т. д.
-
Spacebar — чтобы переключать направление угла.
-
Shift+R — чтобы циклически переключать доступные режимы разрешения конфликтов трассировки: Walkaround Obstacles, Push Obstacles, Ignore Obstacles и т. д.
-
Ctrl+Shift+Wheel Scroll — чтобы перейти на следующий доступный сигнальный слой и вставить via.
-
Shift+F1 — чтобы отобразить список сочетаний клавиш интерактивной трассировки.
-
-
Во время трассировки сегменты дорожек отображаются по-разному (как показано на изображениях ниже):
-
Solid — сегмент размещён.
-
Hatched — штрихованные сегменты предлагаются, но не зафиксированы; они будут размещены, когда вы щёлкнете.
-
Hollow — это так называемый look-ahead сегмент; он позволяет понять, где должен закончиться последний предлагаемый сегмент. Этот сегмент not размещается при щелчке, если только следующий щелчок не завершит трассу. В этом случае срабатывает опция Automatically Terminate Routing и переопределяет поведение look-ahead по умолчанию. Режим look-ahead можно включать/выключать сочетанием
1во время трассировки.


Сплошные сегменты размещены, штрихованные — предложены, но не зафиксированы, а полый — это look-ahead сегмент. -
-
Отличная функция, помогающая визуализировать доступное пространство для трассировки, — возможность отображать границы зазора вокруг всех объектов других цепей Используйте сочетание
Ctrl+W, чтобы включать и выключать отображение границ зазора. Когда функция включена и выполняется трассировка цепи, все объекты других цепей показывают границу зазора, определённую применимым электрическим ограничением clearance. Пересекать эту границу во время трассировки невозможно. -
Во время трассировки множество полезных сведений, включая имя цепи и текущую настройку ширины, доступно в Heads-Up display и в строке состояния
-
Вместо того чтобы трассировать до целевой площадки вручную, можно нажать
Ctrl+Click, чтобы использовать функцию Auto-Complete и поручить движку трассировки попытаться проложить всё соединение целиком. Auto-complete ведёт себя следующим образом:-
Он выбирает кратчайший путь, который может быть не лучшим, поскольку нужно всегда учитывать пути для других соединений, которые ещё предстоит проложить. Если вы находитесь в режиме Push, auto-complete может сдвигать существующие трассы, чтобы достичь цели.
-
На более длинных соединениях путь auto-complete может быть доступен не всегда, поскольку маршрут прокладывается по участкам, и полное сопоставление между исходной и целевой площадками может оказаться невозможным.
-
Также можно выполнить Auto-complete (
Ctrl+Click) непосредственно по площадке или по линии соединения.
-
Единственного решения для трассировки платы не существует, поэтому неизбежно, что вы захотите изменить трассировку. Редактор PCB включает функции и инструменты, которые помогают в этом. Есть два подхода: перетрассировать (reroute) или перерасположить (rearrange).
-
Reroute — выберите команду Route » Interactive Routing и начните трассировку в любой точке существующей трассы, чтобы заново определить путь соединения. Функция Loop Removal автоматически удалит любые избыточные сегменты дорожек (и via), как только вы замкнёте петлю и щёлкнете правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы указать, что завершили.
-
Rearrange —
Click, Hold&Dragдля интерактивного сдвига или перетаскивания сегментов дорожек по плате.
Узнайте больше о трассировке PCB: Трассировка PCB.
Размещение полигонов
Чтобы покрыть сигнальный слой PCB большой областью меди, можно использовать заливку полигоном (polygon pour). Polygon pour автоматически обтекает существующие объекты, подключаясь только к объектам той же цепи, что и polygon pour. Зазоры и свойства подключения управляются применимыми правилами проектирования Clearance и Polygon Connection Style.
Чтобы разместить polygon pour:
- Выберите команду Place » Polygon Pour в главном меню.
-
Во время размещения можно нажать клавишу Tab, чтобы открыть панель Properties и настроить свойства размещаемого полигона: цепь (net), слой, режим заливки и т. д. По завершении нажмите кнопку
 в рабочей области, чтобы вернуться в режим размещения.
в рабочей области, чтобы вернуться в режим размещения.
- Расположите курсор и щёлкните, чтобы зафиксировать начальную вершину polygon pour.
-
Переместите курсор, чтобы разместить вторую вершину, и щёлкните для её установки.
- Продолжайте перемещать мышь и щёлкать, чтобы размещать следующие вершины.
- После размещения последней вершины щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы замкнуть и завершить размещение polygon pour. Нет необходимости замыкать форму полигона вручную, так как редактор PCB автоматически завершит форму, соединив начальную точку с последней размещённой точкой.
- Продолжайте размещать следующие polygon pour или щёлкните правой кнопкой мыши, чтобы выйти из режима размещения.
Если polygon pour изменён (например, изменена его форма или свойства), его необходимо перезалить (repour), чтобы изменения отобразились. Чтобы выполнить repour полигона, нажмите кнопку Repour в верхней части панели Properties, когда полигон выбран.
Узнайте больше о polygon pour: Полигоны на сигнальных слоях.
Выполнение проверки правил проектирования
Редактор печатных плат предоставляет функции проверки правил проектирования (DRC), позволяющие убедиться, что ваш проект соответствует включенным правилам проектирования.
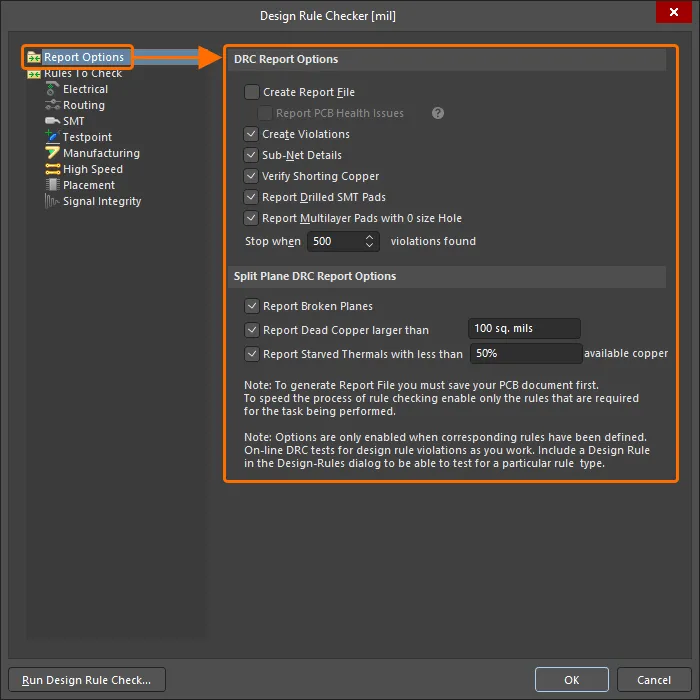
Настройка проверки правил проектирования выполняется в диалоговом окне Design Rule Checker , доступ к которому осуществляется через команду Tools » Design Rule Check в главном меню.
-
Щелкните пункт Report Options в дереве слева в диалоговом окне, чтобы настроить дополнительные параметры, доступные при запуске пакетной проверки DRC.
-
Щелкните пункт Rules to Check или пункт конкретной категории правил, чтобы загрузить в диалоговое окно список типов правил и при необходимости включить каждый тип правил для Online и/или Batch DRC:
-
Online DRC – проверка выполняется в реальном времени по мере проектирования.
-
Batch DRC – проверка выполняется как пакетный процесс при нажатии кнопки Run Design Rule Check в диалоговом окне; результаты выводятся на панели Messages и при необходимости формируется отчет.
-
При запуске Online или Batch DRC обнаруженные нарушения правил будут обозначаться в рабочей области (с использованием пользовательской графики нарушений и/или наложения нарушений). Ниже показаны некоторые примеры нарушений в рабочей области:

Дорожки, нарушающие правило Width. Нарушение обозначено и пользовательской графикой нарушений, и наложением нарушений.

Дорожка, нарушающая правило Net Antennae. Нарушение обозначено пользовательской графикой нарушений.
Вы можете настроить, как нарушения разных типов правил отображаются в рабочей области, на странице PCB Editor – DRC Violations Display page диалогового окна Preferences.
На основе информации о том, насколько сильно нарушено правило, вы можете решить, как лучше устранить нарушение. Например, если ограничение минимальной перемычки паяльной маски (solder mask sliver) задано как 0,25 мм, а фактическая перемычка составляет 0,24 мм, то ситуация не так плоха, и, возможно, вы сможете скорректировать ограничение, чтобы принять это значение. Но если фактическое значение перемычки равно 0,02, то, вероятно, это не та ситуация, которую можно решить изменением ограничения.
-
Подробности приводятся на панели Messages. Указывается фактическое значение вместе с заданным значением (например, 0.017mm < 0.254mm).
-
Также можно щелкнуть правой кнопкой мыши по нарушению и открыть подменю Violations, чтобы посмотреть, какое ограничение нарушено и при каких условиях возникло нарушение
-
Редактор печатных плат также включает удобные инструменты измерения, позволяющие измерять расстояние между двумя точками, измерять выбранные объекты (длину выбранных дорожек и дуг), а также измерять расстояние между двумя примитивами. Подробнее см. на странице Measuring Distances on a PCB.
Панель PCB Rules And Violations — отличная функция для поиска и понимания условий нарушений. По умолчанию она показывает [All Rules] в списке Rule Classes. Определив интересующий тип правил, выберите соответствующий класс правил, чтобы в нижней части панели отображались только эти нарушения. На панели приводятся тип нарушения, измеренное значение, ограничение и объекты, которые нарушают правило. Обнаруженные нарушения правил для выбранного класса правил или конкретного правила также перечислены в области Violations панели. Щелкните запись нарушения, чтобы подсветить нарушение в рабочей области в соответствии с настройкой в верхней части панели: Mask/Dim/Normal, Select, Zoom. Дважды щелкните по нарушению, чтобы открыть диалоговое окно Violation Details.

DRC также можно запускать для всех правил, правил определенного типа или конкретного правила, щелкнув правой кнопкой мыши по соответствующему элементу на панели PCB Rules And Violations и выбрав команду Run DRC.

Запускайте DRC прямо с панели PCB Rules And Violations. Здесь показан запуск DRC для всех определенных правил Clearance.
Узнайте больше о DRC: Design Rule Check (DRC).
















 ).
). ).
).


 ).
). Локализовано с помощью ИИ
Локализовано с помощью ИИ